Performance in 2024
-
 1642Held 1642 community meetings
1642Held 1642 community meetings -
 19,490Received 19,490 visits from stakeholders
19,490Received 19,490 visits from stakeholders -
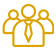 10,000More than 10,000 community members visited us
10,000More than 10,000 community members visited us
Community Engagement
We are committed to establishing meaningful, constructive dialogue with local communities, understanding and taking action on their concerns and demands. Hearing and responding to our stakeholders’ expectations and requests is very important to us, and we resolve any complaints and grievances raised in a thorough manner and through open and transparent communication mechanisms.
Targets and Performance
Performance in 2024



Community Engagement and Communication Framework
Zijin Mining’s Community Engagement and Communication Framework
Grievance and Communication
In accordance with the criteria set in the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights for judging the effectiveness of grievance mechanisms, we regularly review the effectiveness of our communication and grievance mechanisms, make suggestions for improvement and report on progress to stakeholders in a timely manner. This is aimed at developing a positive and efficient two-way communication and feedback mechanism.
UNGPs Criteria for Evaluating Effectiveness of Grievance Mechanisms